Radioactivity
Question 1 radioactivity
Which statement is correct?
Question 2 Alpha-particle, Beta-particle, Gamma-rays
| property | $\alpha$-particle | $\beta$-particle | $\gamma$-ray |
| nature | 2 protons + 2 neutrons | an electron | electromagnetic wave |
| masss | $4\:$u | $0.00055\:$u | $0$ |
| speed | 5 % the speed of light | 98 % the speed of light | speed of light |
- Describe the charge of $\alpha$-particles, $\beta$-particles and $\gamma$-rays.
- Describe how $\beta$-particles are generated.
- Describe the existence of $\gamma$-rays.
- ${^{238}_{92}\text{U}}$ undergoes decay by emitting an $\alpha$-particle and then a $\beta$-particle. State the change in mass of the nuclide.
- Explain the meaning of isotopes.
- charge of $\alpha$-particles: $2e$,
charge of $\beta$-particles: $-e$,
charge of $\gamma$-rays: $0$ - Beta-particles (electrons) result by the decay of a nucleon into a proton.
- Gamma rays result from atoms with excited state during decay by turning into non-excited state.
- mass: $m_{Pb}=238\:\text{u}$, $m_{Th}=234\:\text{u}$, $m_{Pa}=234\:\text{u}$
- Isotopes are atoms that have the same proton number, but different number of neutrons.
Question 3 radioactive decay
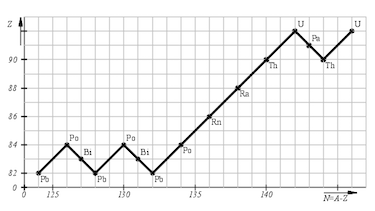
- Draw the decay chain of ${^{238}_{92}\text{U}}$.
- Justify why isotope with a short half time are less numerous.
- Lead Pb has a proton number of 82. Write the nuclear equation for the emission of an $\alpha$-particle from polonium-214 ${^{214}_{84}\text{Po}}$.
- Cobalt Co has a proton number of 27. Write the nuclear equation for the emission of an $\beta$-particle from iron-56 ${^{56}_{26}\text{Fe}}$.
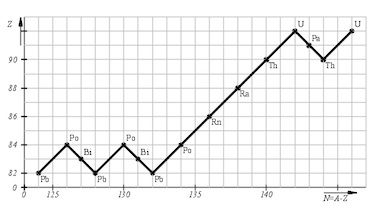
- decay chain lead-238:
${^{238}_{92}\text{U} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{234}_{90}\text{Th} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: {^{234}_{91}\text{Pa} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: $ $ {^{234}_{92}\text{U} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{230}_{90}\text{Th} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{226}_{88}\text{Ra} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: $ $ {^{222}_{86}\text{Rn} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{218}_{84}\text{Pa} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{214}_{82}\text{Pb} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: $ $ {^{214}_{83}\text{Bi} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: {^{214}_{84}\text{Po} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{210}_{82}\text{Pb} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: $ $ {^{210}_{83}\text{Bi} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: {^{210}_{84}\text{Po} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{206}_{82}\text{Pb}}$ - Isotope with a short half time are less numerous since they decay faster then their previous isotope.
- decay of polonium-214: ${^{214}_{84}\text{Po} \xrightarrow[]{\alpha}}\: {^{210}_{82}\text{Pb}}$
- decay of iron-56: ${^{56}_{26}\text{Fe} \xrightarrow[]{\beta}}\: {^{56}_{27}\text{Co}}$
Question 4 Exponential decay
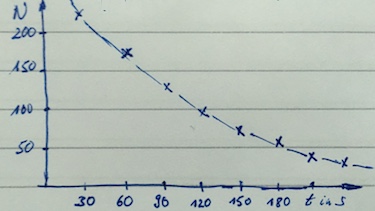
The following count rate from a radioactive source was measured.
| $t$ in s | 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 |
| count rate in 1/s | 160 | 110 | 71 | 47 | 32 |
- Plot a graph of the count rate versus time.
- Use the graph to determine $\lambda$.
- Determine the half life $t_{1/2}$.
- Calculate the time for $N(t)=N_0/4$.
- count rate versus time:

- Determine the decay constant $\lambda$ from graph:
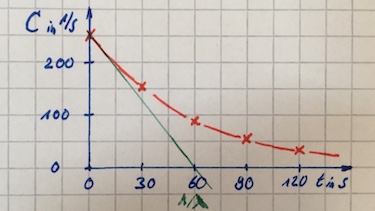
Determine the decay constant $\lambda$ by calculation:
$152=250\cdot e^{-\lambda \cdot 30\:\text{s}} \Leftrightarrow \lambda = 1/60\:1/\text{s}$ - $t_{1/2}=-60\cdot ln(1/2)\:\text{s}$
- $t_{1/4}=-60\cdot ln(1/4)\:\text{s}$
Terms and phrases
| atomic nucleus | The central area of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons. |
| nuclide | An atom with specific number of protons and neutrons. |
| radioactivity | Radioactivity refers to the property of an unstable nucleus by emitting ionized rays and particles. |
| radioactive decay | The nucleus is changing into a different nucleus while emitting quantum like alpha-, beta- particles or gamma-rays. |
| count rate$C$ | The number of measured radioactive particles per second. |
| exponential decay | If a radioactive material undergoes decay the number of nuclei $N$ decreases by an exponential function $N(t)=N_0\cdot e^{-\lambda t}$. $N_0$ the initial number of nuclei, $\lambda$ the decay constant. The count rate $C$ or the activity $A$ also follow this law. |
| decay constant $\lambda$ in 1/s | $1/\lambda$ is the time where the number of nuclei is reduced by 37 %. It also refers to the initial gradient of the decay-graph. |
| half life $t_{1/2}$ | The half life $t_{1/2}$ refers to the time where the numbers of nuclei are divided by two. |
| applications of radioactivity | nuclear power plants, X-rays, determine the age of rocks - carbon dating, radio therapy |
© mylime.info